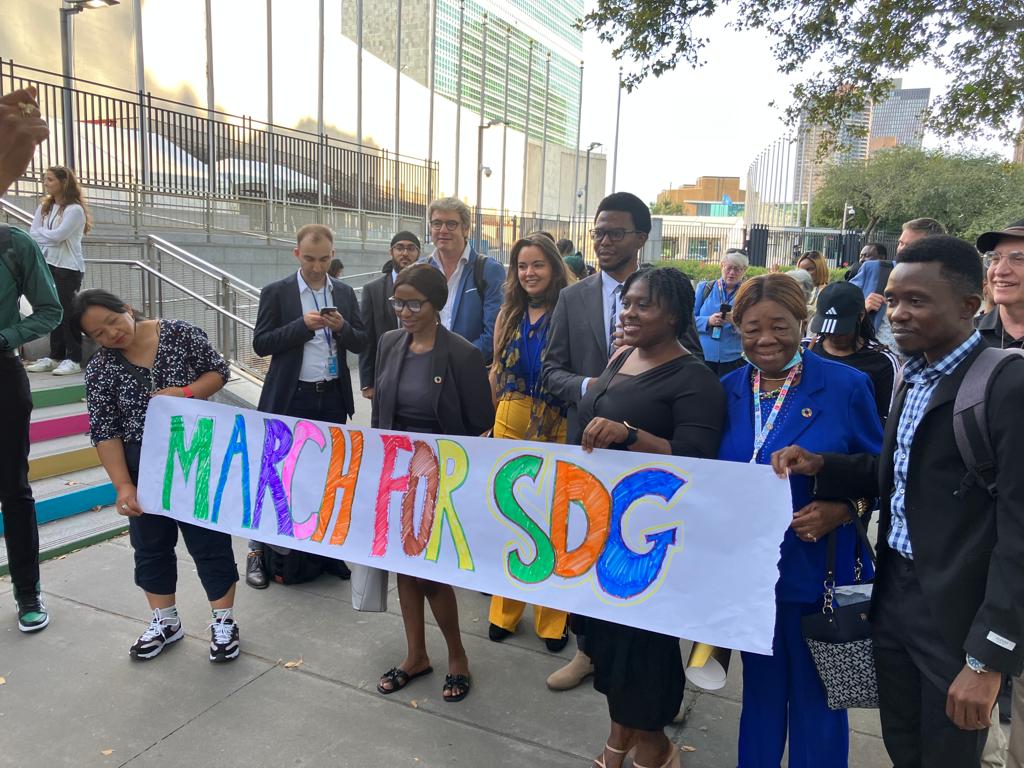Training and workshops for water safety and sanitation within the project “Risk Management in the Water, Sanitation and Microplastics Sector in the Balkans Region”
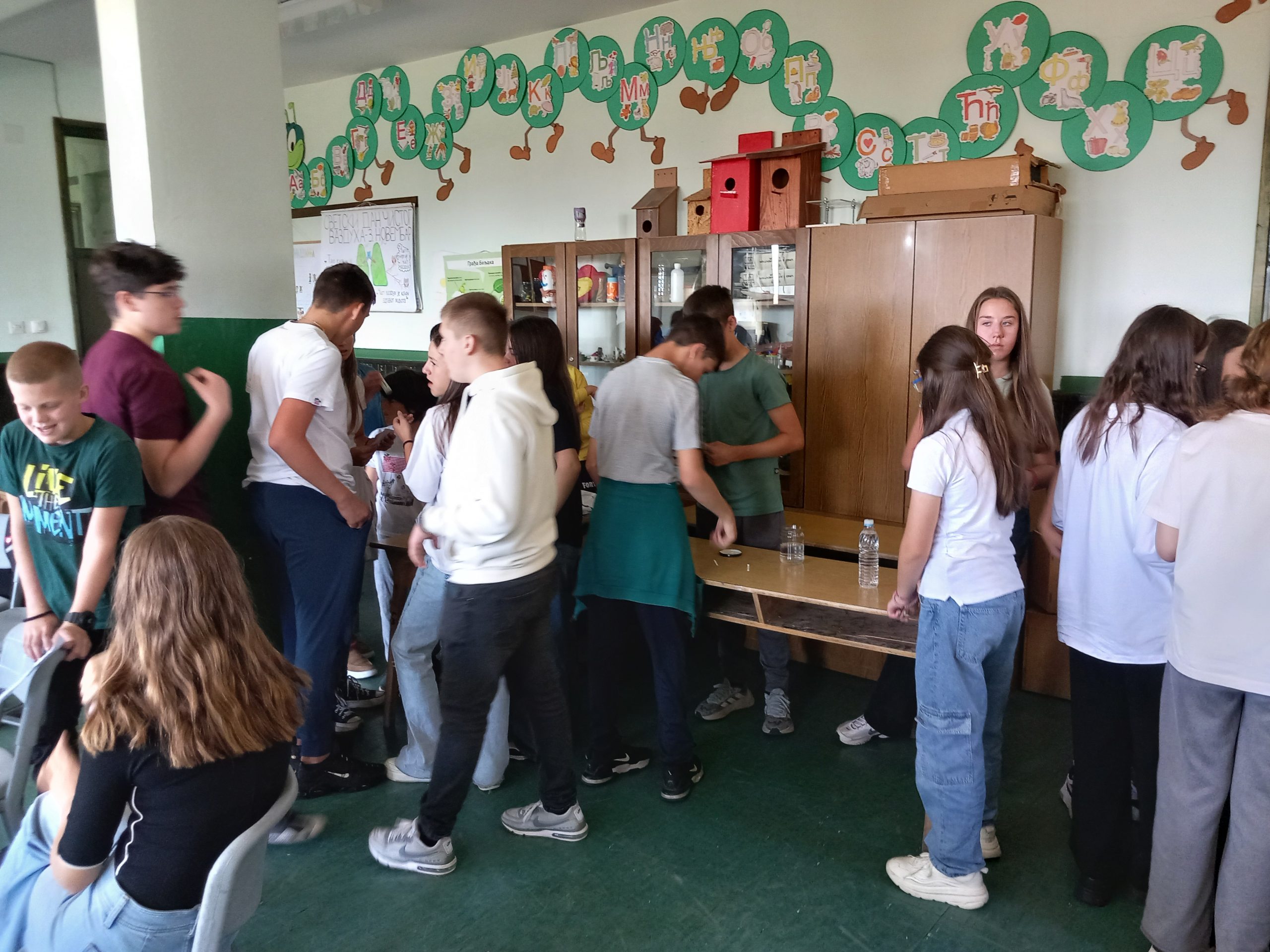
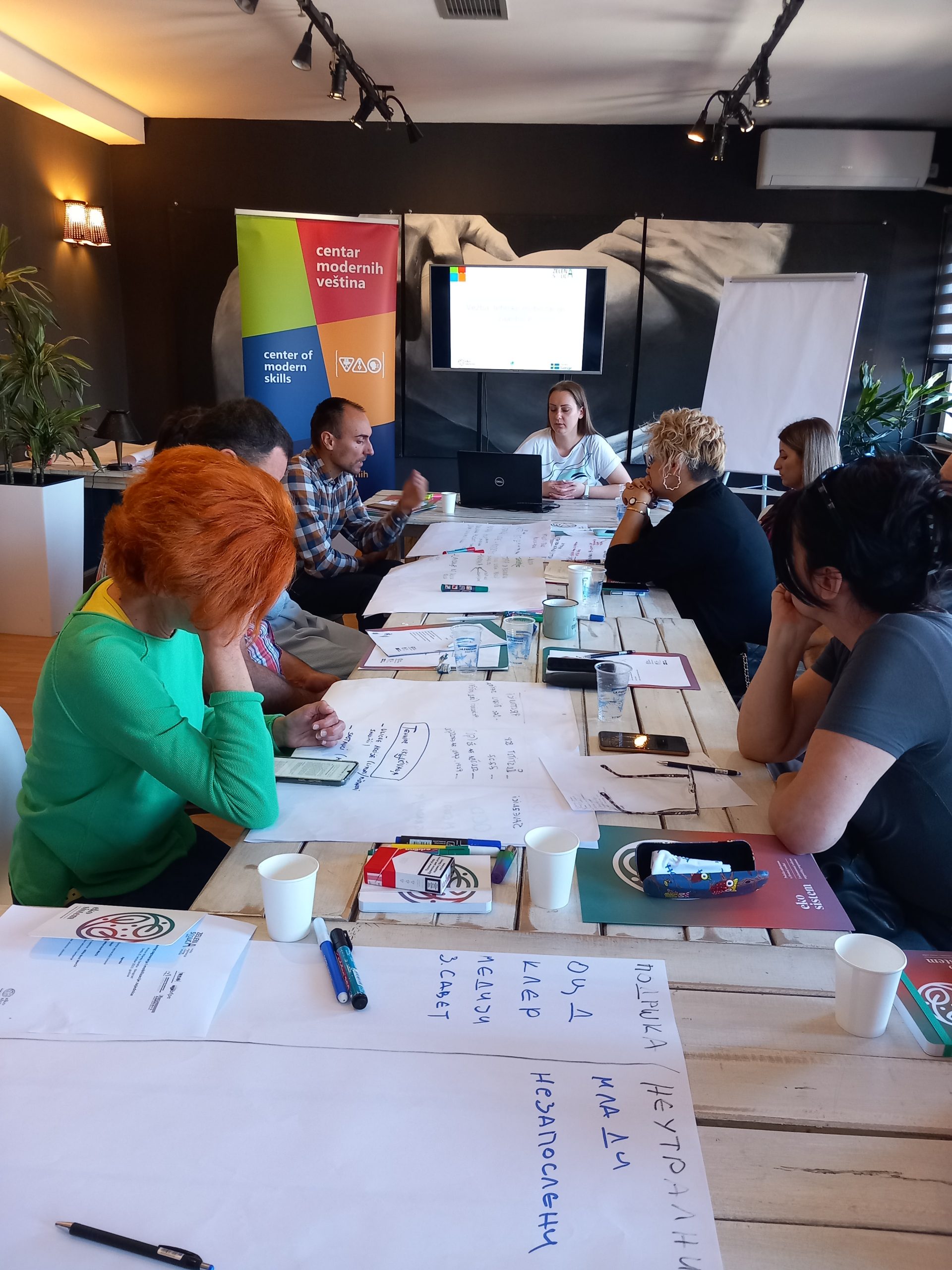
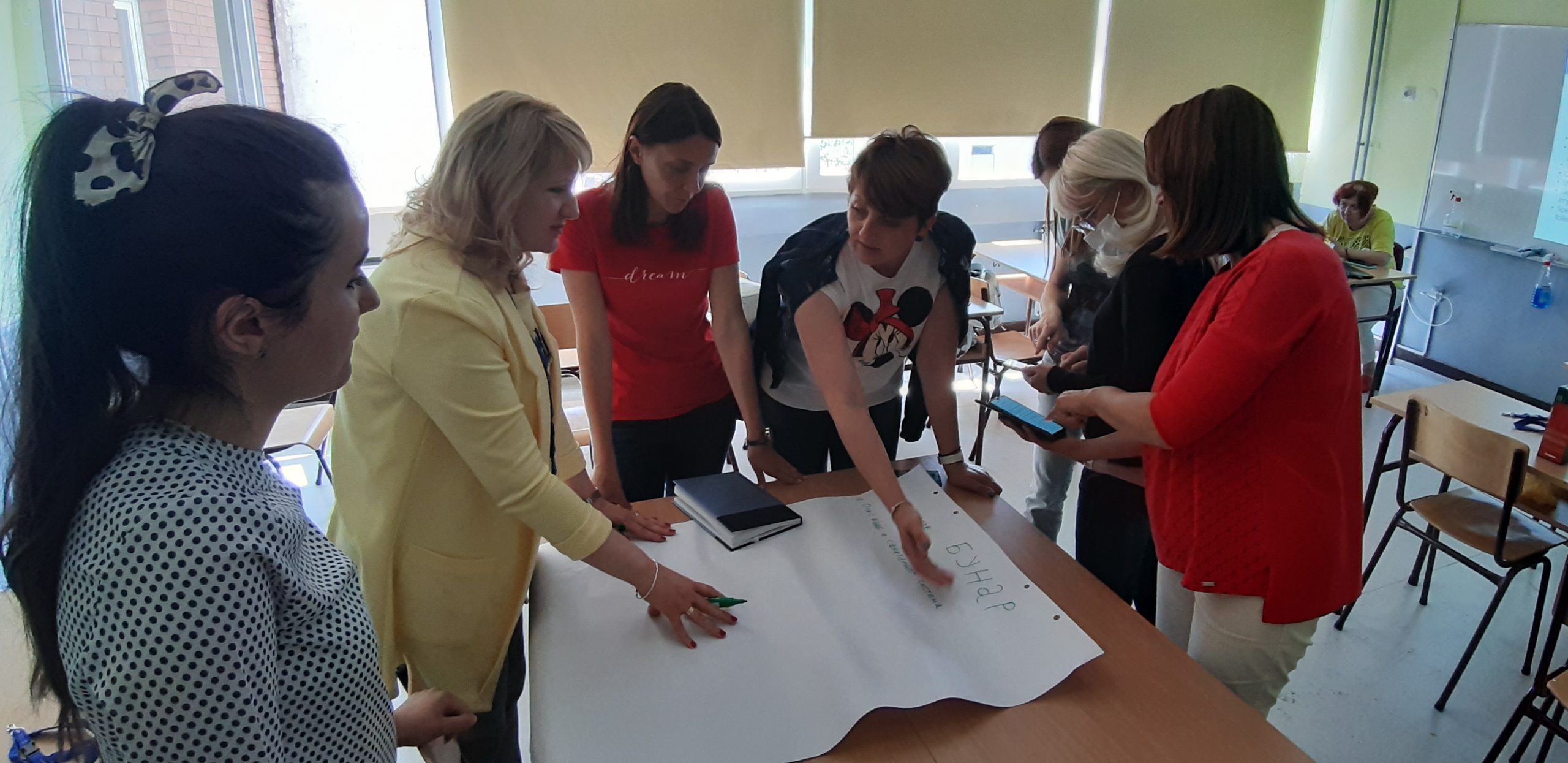
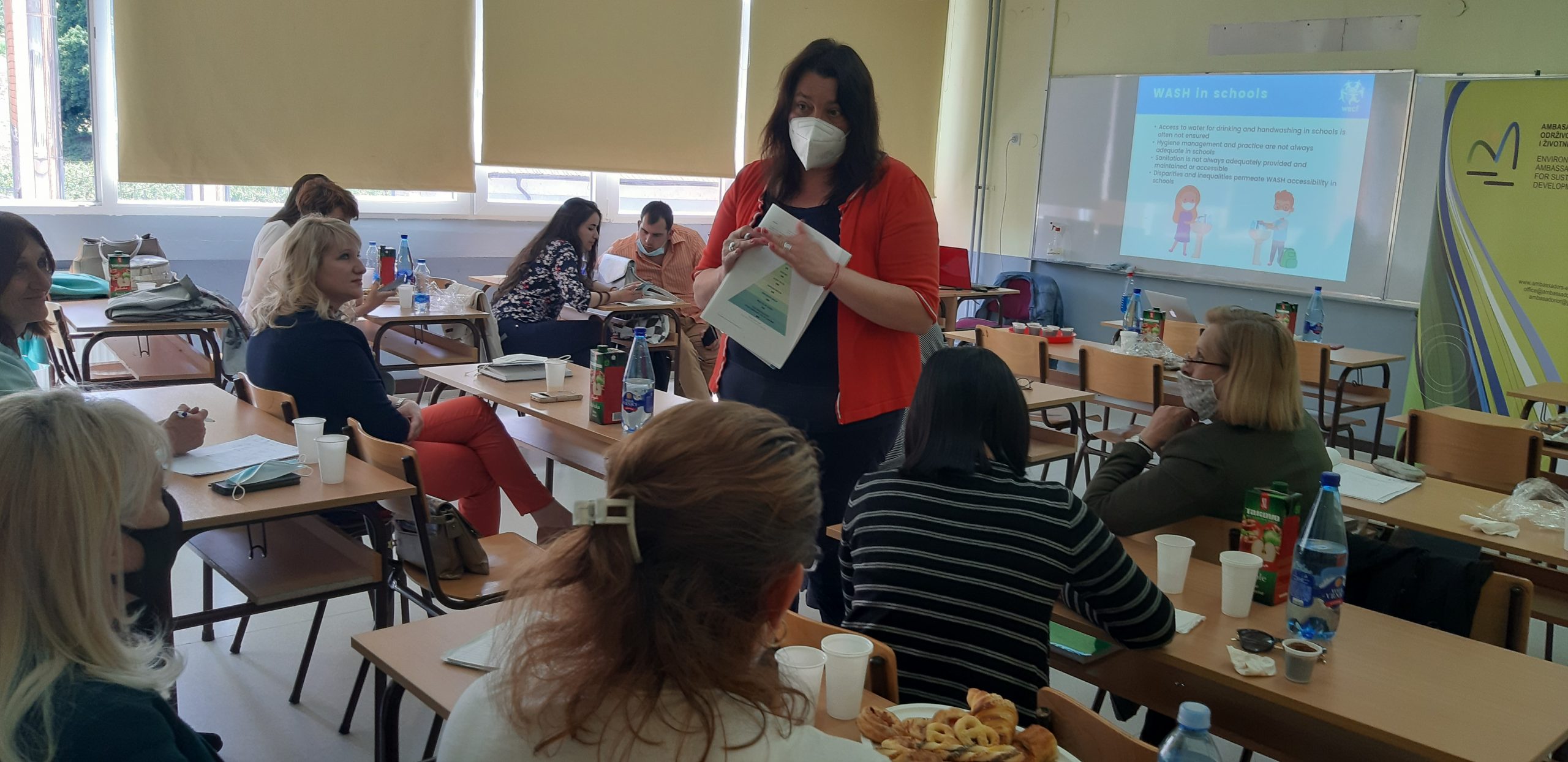
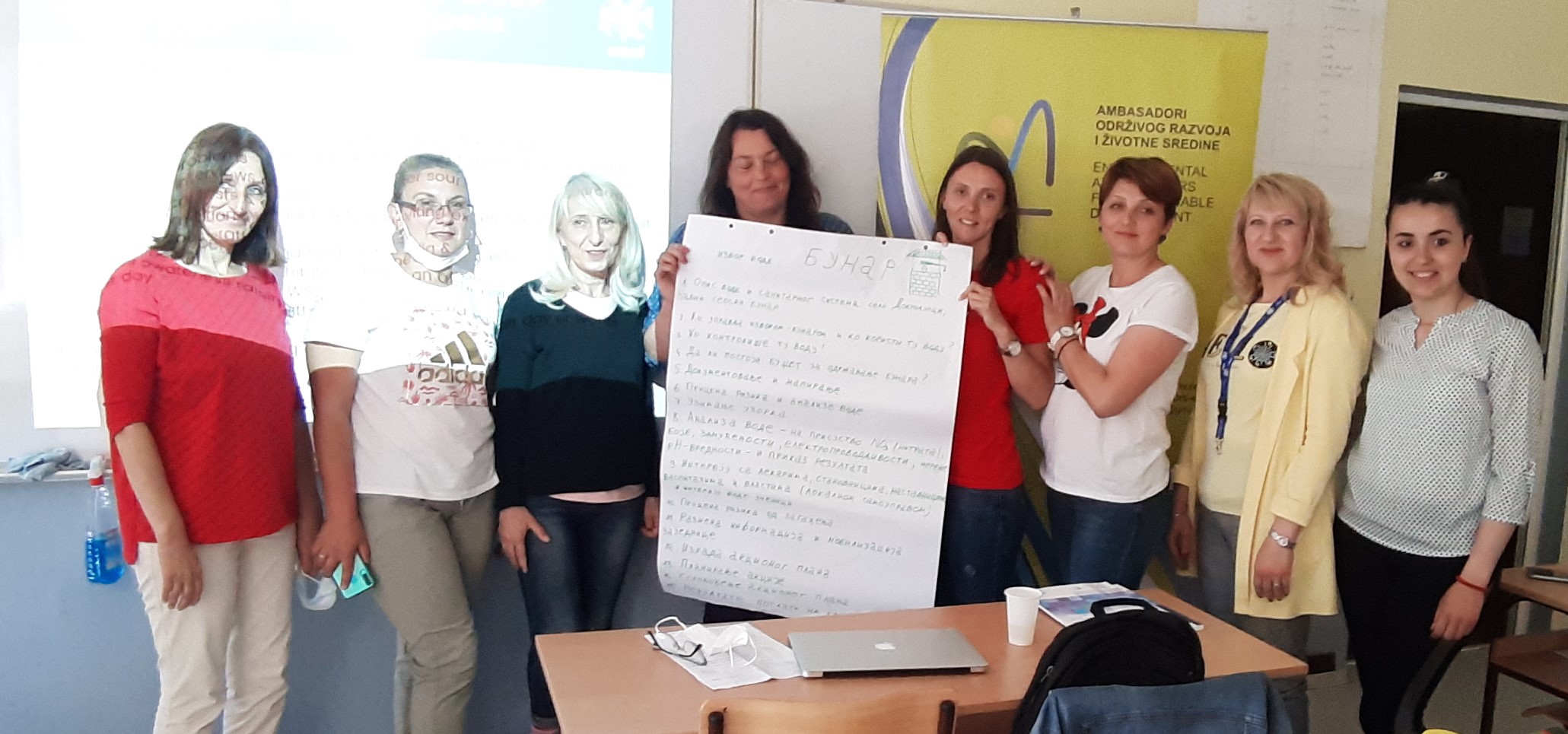
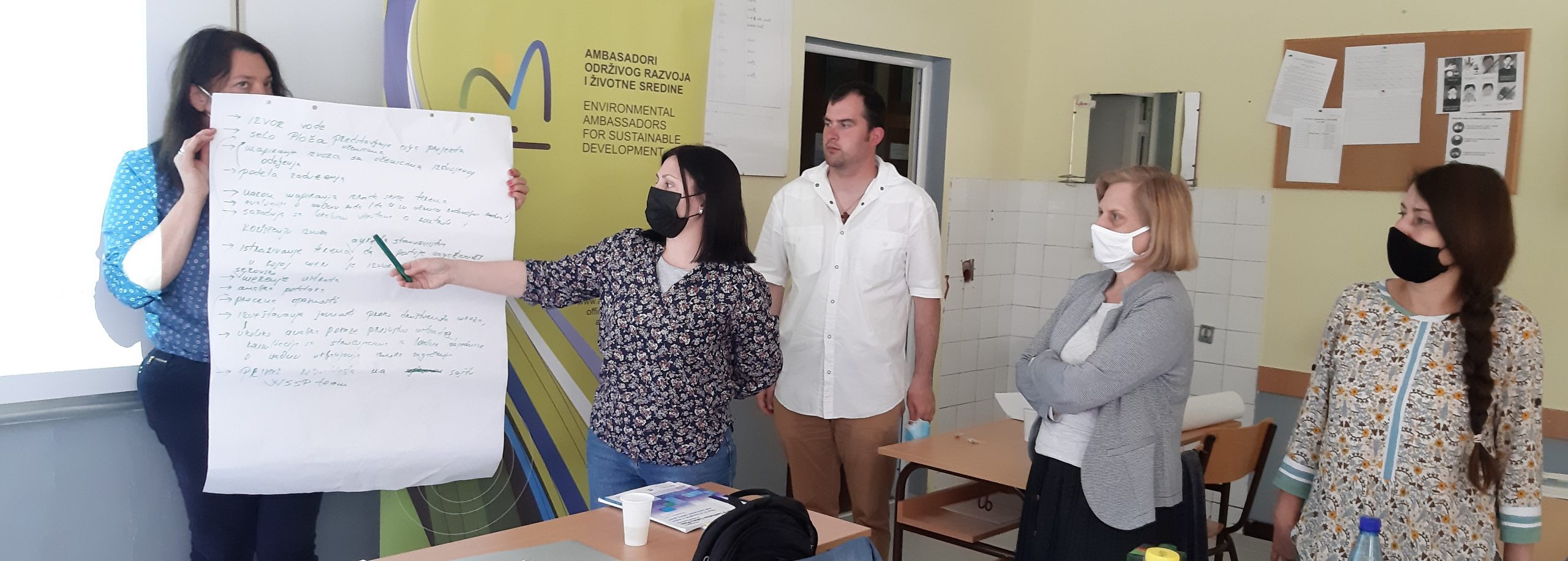
Training and workshops for water safety and sanitation were held for teachers and students in Čajetina, on September 26 and 25, 2024, in cooperation with the elementary school “Dimitrije Tucović” from Čajetina and representatives of the organization “Women Engaged for a Common Future” (WECF) from Germany. The training aimed to increase the participants’ knowledge of the Water Safety and Sanitation Plan (WSSP), menstrual health/hygiene and microplastics about their role and how to implement activities in rural and semi-urban communities in the Balkan region. The material used during the training and workshop is the WSSP Compendium, as well as materials for microplastic research available in English, Albanian, Serbian, Macedonian and Bosnian
The lecturers were Nataša Dokovska, Journalists for Human Rights (JHR), for menstrual hygiene and “Hour on Water”; Eli-Maria Lud – for microplastics; Bistra Mihajlova, Maria Papateodorou, as WECF WSSP representatives; and Aleksandra Mladenović, Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development (EASD).
Agenda and materials are posted in Serbian language.
Participants were divided into groups:
- Positive and negative aspects of the local situation of water supply and sanitation – especially in schools and other public institutions,
- Menstrual hygiene – recent activities,
- Microplastics
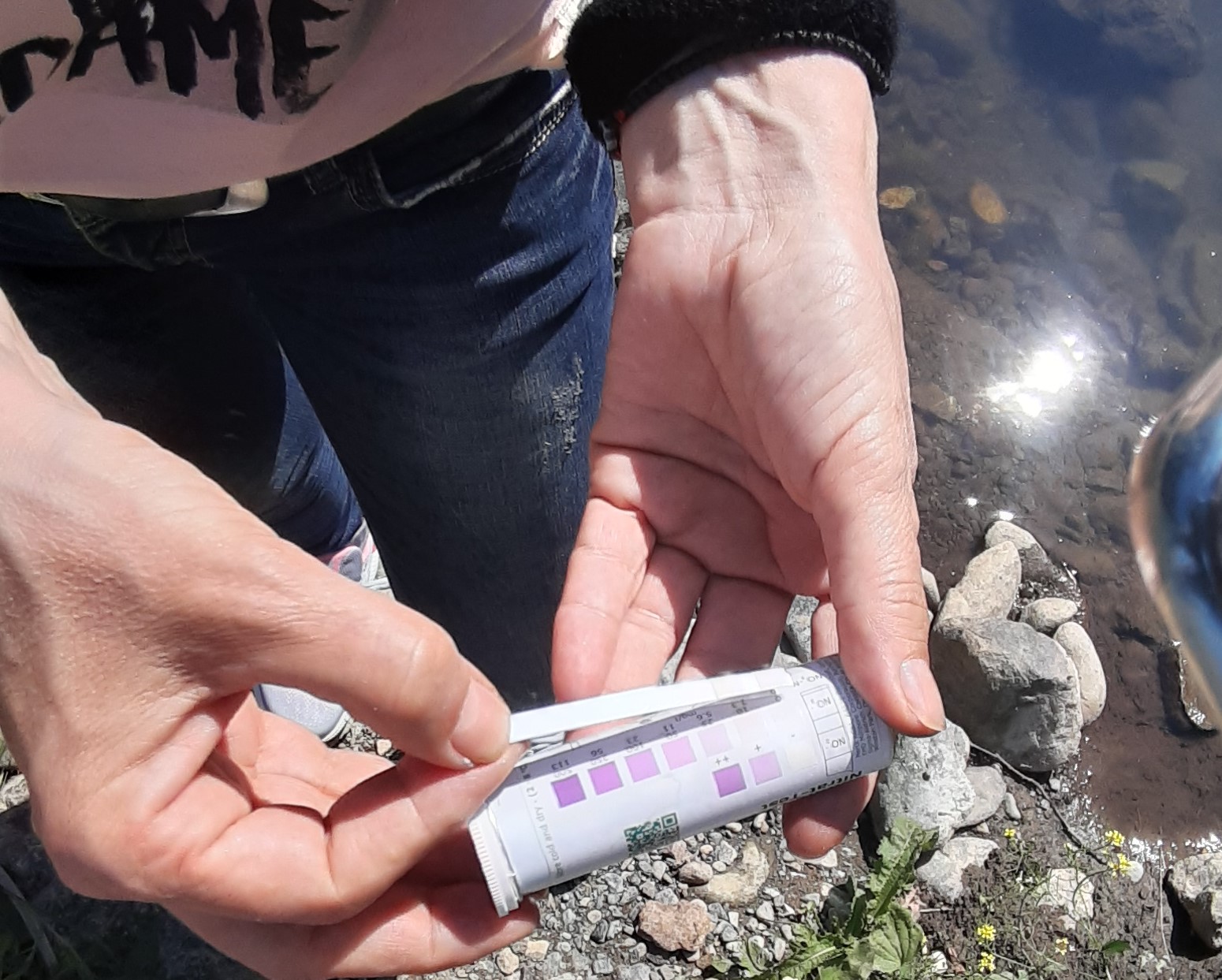
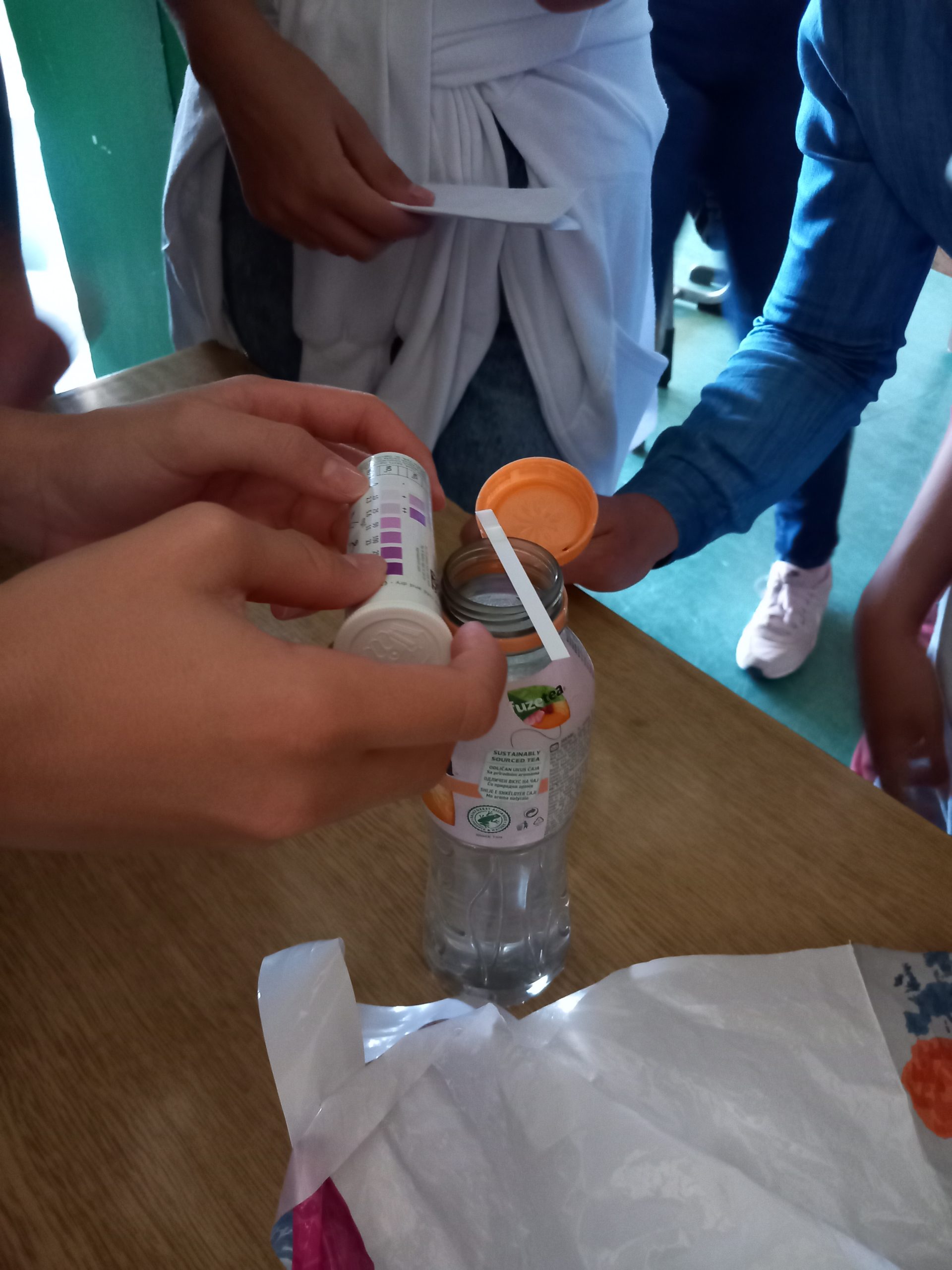
Participants had the opportunity to see the level of turbidity on samples of drinking water (100-200 ml) from their village, from a well or spring, tap water and check the presence of nitrates by nitrate tests.

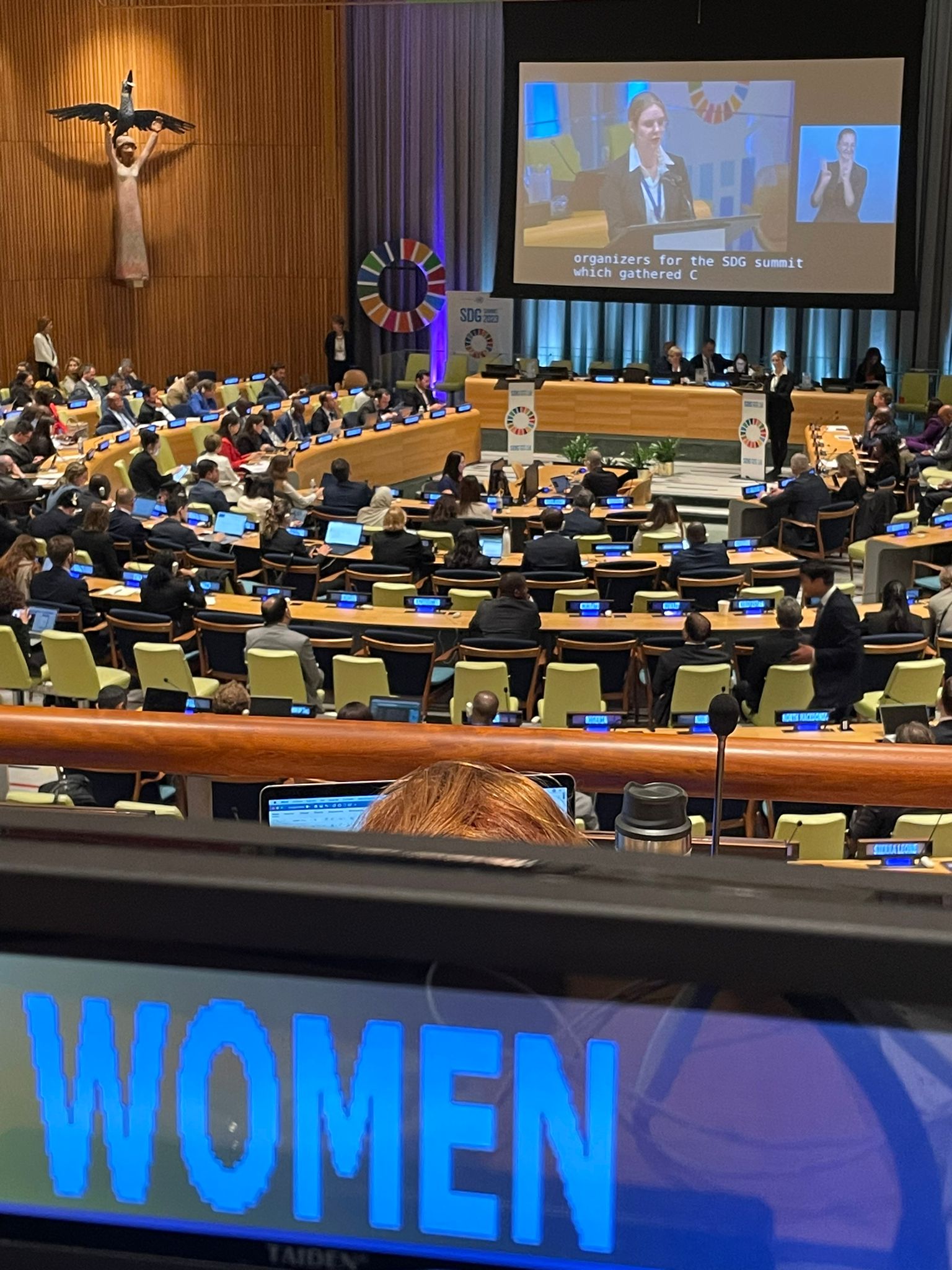
SDG Summit 2023, UN HQ, New York
In the period back to back to the UN General Assembly in New York, the Summit on Sustainable Development Goals was held on September 18 and 19, 2023. Before the Summit, during the weekend of September 16 and 17, the SDG “Action Weekend” was held, as an opportunity for various interested stakeholders, representatives of the UN and member states to meet at the headquarters of the United Nations and present specific commitments and contributions to initiate the transformation of the Sustainable Development Goals from now until 2030.
The activities were divided into two days: “Mobilization Day” on September 16 and Acceleration Day on September 17. During the Mobilization Day, stakeholders from different sectors had the opportunity to gather at the United Nations headquarters and mobilize for the ambitious Sustainable Development Goals Summit and the UN General Assembly’s High-Level Week. “Acceleration Day” focused on high-impact UN initiatives.
Civil society, the private sector, youth, scientists, local and regional governments, feminists and other actors have a key role in the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals. Their participation, contributions and catalytic mobilization are recognized as essential during the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
The President of the Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development Aleksandra Mladenović, attended the SDG Action Weekend and SDG Summit as a representative of an organization that has ECOSOC consultative status and as one of the representatives of the Women’s Main Group at the UN.
The focus of the Sustainable Development Goals Summit was on the fulfillment of the Goals. According to official data, at the global level, only 15% of the goals have been met so far, and we are halfway to the set deadline (2015-2030). It is obvious that, despite the frequent rhetorical glorification of the importance of the Sustainable Development Goals, there is no strong political will to fulfill the Goals, especially of the major world powers, which “hide” behind the success of smaller countries, who care, because the Goals are directly related on their progress, such as reducing poverty, ending hunger, accessing clean water and addressing climate change. The need to change the global “financial architecture” is increasingly being heard, bearing in mind that developing countries are increasingly stagnating, affected by large debts, which often amount to more than investments in key areas, such as education or health in those countries. Young people also raised their voices, because they are beginning to understand that adults are putting a “hot potato” in their hands, under the pretext that their future is already ruined by the present. The youth made it clear that without defined financial means for the Sustainable Development Goals individually, little or nothing will be able to be done in terms of their fulfillment. More at the link: https://www.un.org/en/conferences/SDGSummit2023/SDG-Action-Weekend
As part of the activities of the interested parties, there was also a two-day session of the “Global People Assembly”, where activists from 145 countries gathered and sent a Declaration demanding urgent action from decision-makers in the field of economic and financial justice, climate change, and the environment. social justice and gender equality, protection of civil society, and human rights. More at the link: https://www.peoplesassembly.global/en/
And last but not least, the Summit on the Sustainable Development Goals was held, and a political Declaration was adopted, covering the different and complementary functions of both sessions of the forum under the auspices of the General Assembly – the Summit and the forum under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC ). It seems that this Declaration, as well as the Summit itself, have become only a satisfactory form and “first companion” to the main event in the United Nations, which is the General Assembly. More about the Sustainable Development Goals Summit: https://www.un.org/en/conferences/SDGSummit2023/political-declaration
Kick-off meeting, Sarajevo May 18 and 19, 2023 – Project WSSP
WSSP: Risk management in the water, sanitation, and microplastics sector in the Balkan region
The kick-off meeting on the project “WSSP: Risk management in the water, sanitation, and microplastics sector in the Balkan region” is held in Sarajevo, on May 17th and 18th. Project partners had the opportunity to meet each in person, and to discuss new activities that should be performed in the next two years. The project is run by Women Engage for a Common Future (https://www.wecf.org/wssp/), under the topic of water safety, sanitation and hygiene (WASH). Environmental Ambassadors is a partner from Serbia, and together with other partners from North Macedonia (“Journalists for Human Rights”), Albania (“Milieukontakt” and “Women in Development”), Romania (“Aquademica”) and BiH (“Eko tim”) discussed, among another technical thing, how to put emphasis more on the regional and transboundary component of the project, including funding opportunity for teachers mobility and exchange of experience they gained working in this project and topic in the past. The focus will be on water, sanitation and hygiene, schools, teachers, and students, but also local community members and decision-makers and especially parents, taking into account that one of the project components will deal with more intensive involvement of the children with special needs.
More about the project on this link
Unstoppable conference in Tirana – Women overcoming barriers to success
- Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development participated in the Unstoppable conference dedicated to Women and Leadership
The multi-structured and empowering conference dedicated to Women and Leadership is organized in Tirana, from February 20th to 23rd, 2023. Organizer is the Western Balkan Fund (WBF), with the support of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan and the Visegrad Fund. Every February and March, the WBF with the support of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan hosts an advocacy event by bringing in national, regional & international experts and creating a space of inspiration, connection, and rejuvenation. The purpose of #Unstoppable conference is to foster equal access to leadership in business, government, and non-profit organizations within the Western Balkans, Visegrad regions, and beyond. This event also promotes support and expands initiatives that promote equal access for women and men in development processes.
The conference includes a multitude of topics across the human rights spectrum, enhancing knowledge and strengthening the network of professionals coming from WB6 and V4 regions also unites diverse stakeholders, researchers, stories, and case studies from all over the region in parallel sessions while offering many networking opportunities.
The goal of the Unstoppable is to foster equal access to leadership in business, government, and non-profit organizations within the Western Balkan and V4 regions and beyond. WBF in close cooperation with V4 partners plans to gather around 120 participant’s men and women around both regions and beyond in Tirana since we believe that gender equality should be addressed by both sides, men and women.
ECO-SYSTEM AND “GREEN CHAIR”: PROJECT “CITIES READY FOR CLIMATE CHANGE”
Consultations and a workshop for the preparation of the proposal of the Strategic Plan of the “Green Chair” network were organized within the third cycle of the EKO-SYSTEM support program “Cities Ready for Climate Change”, in October 2023. The lead partner is the Centre for Modern Skills, and the partners are the Aarhus Centre Novi Sad, the BFPE Foundation for Responsible Society and the Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development. The project aimed to improve further the work and strengthen the “Green Chair” network. The topic of the project is adaptation to climate change at the local level.
During the implementation of the project, another activity was consultations held with representatives of local communities: Kruševac, Pirot, Požega, Sremska Mitrovica and Subotica, to encourage advocacy at the local level, related to climate change.
The representative of the Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development, Aleksandra Mladenovic, supported the preparation of a model of a local initiative for the city of Kruševac, which contains measures to mitigate climate change at the local level. As part of the mentoring work, two online thematic meetings were held, with the team for drafting a local initiative. It includes the concept of measures that will be proposed to the local self-government unit. The mentoring work resulted in greater cohesion of the local team, strengthening mutual communication and reaching an agreement on joint climate action at the local level.
Proposal of measures and recommendations for adaptation to climate change and mitigation of the impact of climate change, for local self-government units
General Measures
1. Include a set of measures and recommendations for adaptation to climate change in the development of spatial planning and strategic documents, Development Plans, and Local Environmental Action Plans.
2. Building, strengthening and improving capacities at the municipal level to a) adapt to climate change to introduce adequate measures into policies and decision-making processes at the local level, b) plan and implementation of climate policies, as well as modeling GHG emissions at the local level, and c) data collection, analysis and use (with a focus on the use of GIS), especially those related to river basins, flood maps, water source protection zones, erosion risk zones, etc.
3. Organizing trainings and seminars on available funds for the implementation of projects directly related to climate change (renewable sources, energy efficiency), joint training and seminars to strengthen institutional capacities and improve multisectoral cooperation.
4. Preparation of educational manuals to improve the understanding of the vulnerability of certain sectors to the impacts of climate change and to build resilience and adaptive capacity of the local community.
5. In cooperation with higher levels of government, strengthen the capacities (technical and human) of protection and rescue services at the local level to undertake organized and effective protection and rescue measures.
6. Establishment of an early warning system for the management of extreme climatic events (for all types of climate hazards: floods, droughts, landslides, forest fires, etc.).
7. Use of digital technologies to monitor extreme climatological situations (e.g. drone monitoring, real-time monitoring, etc.).
8. Establish a single database on droughts, floods and landslides and their damage.
9. Adapt Local Fire Protection Plans in the context of adaptation to climate change; ensure reserve amounts of water, by building or installing water tanks, etc. for effective fire protection (especially in open spaces).
Measures by sector
– Agriculture
1. To improve the knowledge of farmers about the impacts of climate change and to introduce them to examples of good practice from the countries of the European Union, but also from the surrounding countries.
2. In organized agricultural production, establish a hail protection system.
3. Improve irrigation infrastructure and ensure sufficient water for irrigation of arable land, in particular for agricultural production that takes place outdoors and is therefore exposed to weather conditions.
4. Receive and capsulate large waters when they exist and make them available in conditions of need through the construction of artificial reservoirs, which, in addition to the production of electricity, also create conditions for the development of tourism, provide flood protection of the downstream area and provides water for irrigation.
5. Implement measures to improve cooling in agriculture (construction of shelter from the sun, adequate accommodation, installation of fans and sprinklers).
6. Subsidize small agricultural producers, especially in the context of reduced incomes and agricultural yields during dry periods.
7. In agriculture, encourage the use of adequate varieties that are more tolerant to heat and drought, change crop patterns, target land management practices, farm structure, and adaptive capacity of farmers.
8. Application of measures aimed at preventing plant diseases, soil heating, etc.
9. Create the conditions and strengthen the awareness of farmers for adequate management of agricultural waste to reduce emissions from methane.
– Forestry
1. Maximize illegal logging control and implement forest health protection measures (occurrence of pathogenic fungi, occurrence of forest fires, define measures in response to snowstorms, wind gusts, frosts, etc.).
2. Intensify afforestation in landslide-prone areas and land erosion to reduce the risk of new landslides.
3. Establish comprehensive monitoring of areas at risk of erosion and landslides, with the preparation of plans and maps and action plans for prevention and control over their implementation.
– Civil engineering
1. To reduce the risk of landslides, establish continuous monitoring and documentation of illegal and unplanned construction of residential and other buildings and consistently implement regulations governing construction conditions.
– Water management
1. Plan the construction of a system for connection to the sewage network and wastewater treatment plants
2. Provide for continued investment in preventive protection and rescue measures, as well as full coordination with all actors having an impact on floods.
3. Procurement of adequate material and technical means and equipment is important for the provision and organization of all measures that affect the degree of vulnerability of people and material goods from floods.
4. To ensure timely and complete information to citizens about all measures and actions taken by the municipality to reduce the risk of floods, as well as to raise awareness of citizens about the possible consequences of floods.
5. Establishment of uniform inter-municipal and regional flood protection measures and a unified system of warning and notifying the competent structures of the upcoming danger, as well as the need to build a common (single) management system for hydropower facilities that have a regional character.
– Nature protection
1. Application of Nature Based Solutions, such as the maintenance and restoration of natural aquatic ecosystems (e.g. rivers, connecting river channels and meanders), afforestation, restoration and maintenance of grasslands, buffer zones, adequate land management, etc., because nature-based measures are more effective than technical infrastructure for flood protection (embankments, canals, etc.), both in environmental and economic terms.
– Waste management
1. Implement measures to reduce the waste that is deposited and adequate collection of municipal waste (collection networks in rural areas, construction of recycling yards, procurement of specialized equipment for waste collection, as well as activities to educate and raise awareness among the local population about the importance of this topic).
-Gender equality and human rights
1. At the local level, work on linking gender equality and climate change, as well as the realization of equal rights for all, especially vulnerable groups (e.g., youth, Roma, women, persons with special needs…), by implementing climate change mitigation measures.
Call to action for a tomorrow without toxics
Sign the Call to Action here:
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSecU8_1QRK983bsB1s92c0sHyVBv
adDWW2dW–T_46_JiWjgg/viewform
Urgent call for a strong SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework ensuring sound chemicals and waste management!
Increasing chemical production, use of harmful chemicals, pollution, and waste are turning into a third planetary crisis[1], beside the climate and biodiversity crises, and at the same time exacerbating them. There is an urgent need for solution-focused actions along the whole lifecycle of chemicals and waste, addressing the threats to human health and the environment – from the enormous use of chemicals, poor chemicals and waste management, to the ever-increasing production and raw material extraction. The undersigned organizations stand together in urgently calling
on governments, industry, and other stakeholders to work towards a tomorrow without toxics. We urge them to actively reduce their chemical footprint and make prevention, reduction, and sound management of chemicals and waste a priority issue.
The current levels of chemicals used in industrial processes, agriculture and daily life products massively expose people and ecosystems to harmful substances.
Ubiquitous, excessive and often uncontrolled use of chemicals, their improper storage and disposal, and accidents, as well as the amount of waste in general and in particular mismanaged waste lead to harmful substances entering the environment, food chains, and human bodies. They poison air, soil and water, harm wildlife and cause biodiversity loss. Exposure to hazardous chemicals produces reproductive and neurological disorders, causes intergenerational effects, and the loss of livelihoods and food systems, among other things. The burdens fall disproportionately on the most financially oppressed, vulnerable and marginalized groups, such as Indigenous
Communities, people in the Global South, workers in industry and agriculture, women and children. This makes chemicals and waste management a cross-cutting issue.
The Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) and the Dubai Declaration, adopted in 2006 by the First International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM1), aimed to achieve sound management of chemicals and waste throughout their life cycle by 2020.[2] Now, at the beginning of the year 2022, we see an even more urgent need for action. SAICM has identified important issues and created a multi-sector platform and multi-stakeholder process for action, involving governments, civil society, businesses and academics. However, the overall objective has not been achieved and progress made is insufficient and mainly limited to information collection, while only a few concrete risk reduction measures have been undertaken. Adverse impacts on human health and the environment from raw material extraction, chemical production, use and disposal continue.
There is no time to waste.
We need an agreement for a strong SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework that goes beyond the Dubai Declaration on International Chemicals Management[3] and secures ambitious reduction and prevention of harmful chemicals and waste globally, bringing about real change, including the implementation of safe alternatives. Our vision is a world where chemicals and wastes are no longer a source of harm and where all people live in safe and healthy environments, free from toxic threats to ecosystems and to future generations. We call upon all stakeholders to commit to this goal and to increase engagement, expressing a concrete will to end the poisoning of our world. Put a
SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework urgently into practice as follows:
● Recognize and implement the precautionary and sustainability principles as basic principles and rationale behind all measures. Follow the hierarchy of prevention, elimination and minimization of hazardous substances.
● Include the possibility to stipulate or initiate binding elements for chemicals and waste management throughout the whole lifecycle, including raw material extraction, production, use and disposal of chemicals.
● Set ambitious targets and milestones. Make national action plans binding for all SAICM stakeholders, which particularly promote implementation and monitoring. Include concrete activities to solve the Issues of Concern in SAICM national action plans as well as education and awareness raising measures. Ensure that groups of related chemicals are addressed in the framework and in related action plans
● Establish mechanisms for implementation and progress reporting, and independent monitoring, as well as mechanisms for compliance.
● Realize global implementation on all levels (i.e. local, national, regional and international levels) and ensure this through national action plans. Make a SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework compatible with other global treaties
including a future legally binding Plastics Treaty[4] or a future international regulation on pesticides[5].
● Secure the multistakeholder and multisectoral character of SAICM. Ensure that the negotiation process is carried out in a way that guarantees equal and fair participation of all stakeholders and right holders, as well as the
possibility to bring in contributions, especially from the civil society.
● Guarantee solid, sustainable, and reliable financing by the internalization of external costs, according to the Polluter Pays Principle. This could be achieved through a coordinated tax on chemical feedstocks, levied by the
national governments where the chemicals are produced[6], ensuring and prioritizing the support for developing and emerging countries. Especially civil society organizations, Indigenous Communities, and science, including citizen science, should be eligible for funding. Further options to implement the Polluter Pays Principle are to be explored and implemented.
● Make sure that a SAICM-Beyond-2020 addresses the identified shortcomings of the predecessor framework and in particular, that solutions for all identified Issues of Concern (IoCs) are developed and new IoCs included when they are needed. Current IoCs must be kept until resolved[7]. This includes e.g. a global phase-out of highly hazardous pesticides (HHPs) and their replacement with agroecology in line with ICCM4 resolution, measures to reduce endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDC) exposure for humans and the environment, and transparency and traceability for chemicals in products.
● Guarantee globally equal safety levels for everyone and everywhere. States must ensure the protection of people and the environment through laws and regulations that hold producers accountable along the entire supply chain
and throughout the whole lifecycle. Eliminate unethical and unacceptable double standards.
● Support the approach of a binding Global Minimum Transparency Standard[8] as a first step for chemicals in products and the establishment of labeling according to UNEP SCP guidelines[9]. This can ensure transparency and
traceability, which are, together with the right to know, key requirements for a safe circular economy globally. It further helps to eliminate double standards and dumping of products in countries with less ambitious chemicals legislation, and to guarantee an equal level of safety for everyone everywhere.
● Ensure sensitivity to the different exposition and vulnerability of people and groups of people to hazardous substances, depending on their area of residence, occupation, social and economic status, age, and gender. Consider
that children are particularly vulnerable to hazardous substances and must be protected from being born pre-polluted.
● Better protect women from hazardous chemicals, by implementing gender responsive policies, mainstreaming gender-equality and collecting gender disaggregated data. Recognize and encourage the leadership role of women in society, politics and science, and also in a SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework. Consider that women are more susceptible to harmful chemicals than men and have different windows of vulnerability, e.g. during pregnancy.
They are also exposed differently to toxic chemicals due to their gender roles.
● Recognize the principles and values of the universal human rights[10]. Support all right holders, according to the respective international resolutions and declarations[11].
● Recognize the principles of the Rio-Declaration on Environment and Development and the principles of the Agenda 2030, as basic principles.
● Acknowledge the role of chemicals and waste in the biodiversity and climate crises and take action to address these impacts through decreased chemical production, use and disposal, phase out of harmful substances and
implementation of safe and non-chemical alternatives
Urgent call for a strong SAICM-Beyond-2020-Framework ensuring sound chemicals and waste management!
Training for trainers on water safety and sanitation
Within the project “ Water and Sanitation Safety Planning in the Balkan Region: Albania, North Macedonia, Romania and Serbia (WatSanPlan), FKZ 16EXI4004A, Förderprogramm „Exportinitiative grüner und nachhaltiger (Umwelt-) Infrastruktur“ BMU, the first training for teachers of the Eco-school was held in Aleksandrovac. During the two-day training, teachers from primary schools, secondary school and educators from pre-school were introduced to the possibilities provided by the development of a plan for water safety and sanitation, with special reference to the situation in rural communities. In addition to the theoretical work presented by Bistra Mihajlova, a project coordinator on behalf of project leading organization “Women engage for a common future” (WECF) from Germany, participants had the opportunity to exchange their own experiences related to water safety and sanitation in rural areas, where there are many field-departments of Aleksandrovac schools. The topic of menstrual hygiene and how girls and young women are educated in the current conditions was also raised, with general comments that this topic is still taboo in our area and that little attention is generally paid to this topic, through regular curricular and extracurricular activities.
Representatives of one of the partners in the project from North Macedonia, “Journalists for Human Rights”, Nataša Dokovska and Aleksandra, were guest lecturers, who shared their experiences in many years of struggle related to water safety, sanitation, menstrual hygiene and menstrual health. According to research that has been conducted in North Macedonia, Nataša Dokovska pointed out that almost 30% of women in this country cannot afford menstrual products. In North Macedonia, as it is situation in Serbia, they face insufficient education on this topic and an unwillingness to accept it as something that is biologically normal and impossible to pretend not to exist. Among other things, their association advocates that menstrual hygiene be spoken in a gender-neutral language, instead of “products for female hygiene “to be named as “menstrual products”. It is a problem in general that almost 80% of girls know about the menstrual cycle in communication with friends or older sisters in the family, and less often from their mothers or through the education system. The biggest problem in schools is practically that there are no basic sanitary conditions to help girls and women during the menstrual period, so, according to research „Journalist for Human Rights“ realized, in rural areas girls are forced to stay at home during menstruation and to miss classes.
Discussion among teachers from the Eco-schools in Aleksandrovac, there are no such bad experiences in this municipality. However, the positive sign is that through the biology curriculum for the 6th grade, the topic of the menstrual cycle is dealt with, in which boys and girls participate equally.
So far, no more detailed research on menstrual health and menstrual hygiene has been done in Serbia, except sporadic articles in the media and initiatives from the University that can be found. Under this WatSanPlan project, the initial research related to menstrual hygiene and menstrual health will be realized through the Eco-schools program during the school year 2021/2022. The results will show a general observation of water safety, sanitation and menstrual hygiene, which will enable further research and launch advocacy campaigns towards decision makers, primarily related to the availability of menstrual products for free in selected Eco-schools.
The next activity on the project will be training for Eco-schools students on water safety and sanitation in rural communities.
The project “Water and Sanitation Safety Planning in the Balkan Region: Albania, North Macedonia, Romania and Serbia (WatSanPlan)” is supported by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety and the European Union. The project is managed by the international organization “Women Engage for a Common Future”. In addition to the Environmental Ambassadors for Sustainable Development from Serbia, the project also includes civil society organizations from North Macedonia, Albania and Romania.
Feminist response to Covid19
EASD is organization working across global movements centered on human rights, sustainable development, and
economic and social justice; partner feminist organisations come together in a moment of collective organizing to outline key principles for a just and resilient recovery from the ongoing global pandemic, as well as to track responses and uplift collective action of feminists around the world.
The COVID19 pandemic is upending economies, changing mobility patterns, disrupting social networks, altering informal and formal workplaces and flows, and redefining the concept of essential work and who performs it. EASD already address the issues at EnE20 Conference, and by E-campaign.
KEY PRINCIPLES FOR FEMINIST RESPONSE TO COVID19 are cross-cutting to all these principles is the promotion, protection and fulfillment of human rights and gender equality:
- COVID19 responses must centre the well-being of all people in an intersection manner
- COVID19 responses must ensure the health and safety of all, including ensuring sexual and reproductive health and rights
- COVID19 responses must promote a comprehensive paradigm shift, relying on adequate and equitable financing
- COVID19 responses must be based on and strengthen democratic values
- COVID19 responses must promote a just and equitable transition for people and planet
- COVID19 responses must be guided by cooperation, multilateralism and global justice
EASD at the United Nations in Vienna
 As the organisation with ECOSOC consultative status, EASD in October 2015 had some meetings of the broad spectrum of the work of the UN in Vienna.
As the organisation with ECOSOC consultative status, EASD in October 2015 had some meetings of the broad spectrum of the work of the UN in Vienna.
EASD representatives participated in the Interactive Human Rights Tour and briefing on human rights for children. We support “Your actions count – be responsible traveller”
SDGs as the relevant part of the context within which FEE operates
After a long series of intergovernmental negotiations on various themes,which saw a broad participation from major groups and civil society stakeholders under the guidance of the United Nations State Members, the Goals have been adopted on September 25th at the New York United Nations Summit by 193 Member States. In the same occasion, the UN launched their post-2015 development agenda, in which the Goals are integrated. UN Member States, the civil society and private sector contributors will use this new, universal set of goals, targets and indicators to guide development global efforts over the next 15 years in a concerted international action within the broadest, most ambitious development agenda ever agreed at the global level. The 17 Goals and 169 Targets are meant to be action-oriented, concise and easy to communicate, aspirational, global in nature and universally applicable to all countries, while taking into account the different national realities, capacities and levels of development and respecting national policies and priorities.
The Foundation for Environmental Education with its global network thus needs to frame and highlight its role as a stakeholder and trendsetter in the Sustainable Development process, particularly for environmental, educational and eco-tourism matters. The SDGs will define a relevant part of the context within which FEE operates, thus we are driven to reflect our work in the Goals.
FEE through its mission of fostering awareness, knowledge, participation, commitment, skills, actions and creativity on the environment and on sustainable development, shares the core values behind the set of SDGs. The programmes based on Education for Sustainable Development, such as YRE, Eco-Schools and LEAF show a strong link with the educational Goal (SDG 4) and the Goal on global partnership for sustainable development (SDG 17). FEE’s tourism eco-labels, Green Key and Blue Flag, on the other hand, have a focus on making human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable (SDG 11) and on implementing tools for monitoring sustainable development impacts for tourism (SDG 12.b).
Thus, FEE as an umbrella organisation aims at reaching objectives as indicated in the SDGs:
– “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages” (SDG 3).
– “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote life-long learning opportunities for all” (SDG 4).
– “Ensure availability and sustainable management of water..” (SDG 6),
– “Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all” (SDG 7),
– “Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development” (SDG14), as well as to
– “Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems..” (SDG 15).
– “Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth..” (SDG 8), particularly to “..Implement policies to promote sustainable tourism which creates jobs, promotes local culture and products” (SDG 8.9).
– “Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable” (SDG 11).
– “Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns” (SDG 12).
– “Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts” (SDG 13).
– “..Promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems..” (SDG 15).
– “Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development..” (SDG 16), particularly to build transparent institutions and promote non-discriminatory policies for sustainable development (SDGs 16.6, 16.b) with a positive, proactive, democratic modus operandi and a strong synergic support to civil society and third sector.
– “Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development” (SDG 17) through a geographically spread, multi-stakeholder approach.
Programmes’ overview:
a) YRE: Young Reporters for the Environment is a network of international youth engaged in environmental journalism and Education for Sustainable Development, where the students investigate an environmental problem and report it to the local community, while, at the international level, they may cooperate with young reporters from other countries for sharing information or data, with the aim of proposing a solution and disseminating it.
The most evident link between the Young Reporters for the Environment programme and the SDGs is found in the Goal 4:
“Ensure inclusive and equitable quality educationand promote lifelong learning opportunities for all” and its subparagraphs“..increase … the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship” (SDG 4.4) with the aim of learning to think critically, “ensure all learners acquire knowledge and skillsneeded to promote sustainable development, including among others through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship, and appreciation of cultural diversity and of cultures contribution to sustainable development” (SDG 4.7) for being able to connectwith concrete issues.
The environmental educational programme thus also wish for taking “action to combat climate change and its impacts” (SDG13), specifically for what concerns to “improveeducation, awareness raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning” (SDG 13.3) through active solution-oriented learning. The programme canalso help to“promote mechanisms for raising capacities for effective climate change related planning and management, in LDCs, including focusing on women, youth, local and marginalized communities” (SDG 13.b).
YRE is a network of young people educating for sustainable developmentand environmental issues in general, thus it also supportsthe aim of many other SDGs, such as:
“Promotesustainable agriculture” (SDG 2).
“Promote well-beingfor all at all ages” (SDG 3).
“Achieve gender equality and empowerall womenand girls” (SDG 5).
“Ensure availability and sustainable management of waterand sanitation for all”, supporting and strengthening the participation of local communities (SDG6)
“Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energyfor all”(SDG7)
“Promotesustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all”, developing measures that support creativity and innovation (SDG8)
“Build resilient infrastructure, promoteinclusive and sustainableindustrializationand fosterinnovation”enhancing scientific research (SDG9)
“Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable … Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality, municipal and other waste management”(SDG 11)
“Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns”, raising awareness on sustainable development and lifestyles which are in harmony with nature (SDG12)
“Conserve and sustainably use the oceans seas and marine resources for sustainable development”, aiming to preventmarine pollution and protectmarine and coastal ecosystems (SDG14)
“Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss”, promoting the implementation of sustainable management of the forests (SDG15)
YRE helps to “Promotepeaceful and inclusive societies for sustainabledevelopment..”(SDG16)
YRE can encourage to “..Revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development” (SDG17)
The journalistic piece can influence the local communities to take action on various environmental matters
b) ECO-SCHOOLS: A global student-led change process in Education for Sustainable Development which involves also teachers’ training, integration in the school curriculum, environmental reviews, action plans, monitoring and evaluation, informing and involving the local community, setting an eco-code focusing on the various environmental themes (water, energy, waste, global citizenship..).
The programme is fully in line with the Goals:
“Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all” increasing the number of youth and adults with relevant skills and ensuring that all learners acquire knowledge for promoting sustainable development, developinga culture of peace and global citizenship while upgrading education facilities to child, disability and gender sensitive ones as to provide a safe, inclusive and effective learning environment for all(SDG 4)
“Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable”, strengthening efforts to safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritagewith a focus on schools’ waste management, resource efficiency and climate change mitigation (e.g. Litter Less Campaign) (SDG 11)
“Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development” (SDG 17).
The implementation of the Eco-Schools programme also works towards the achievement of the aim of more SDGs, such as:
“Ensure healthy lives and promote well-beingfor all at all ages” (SDG 3)
“Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all”, improving water quality and water-use efficiency with pollution reduction, minimizing the release ofhazardous chemicals, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater,increasing recycling or safe reuse and ensuring sustainable withdrawals together with the strengthening of the participation of local communitiesfor such purposes (SDG 6)
“Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all” increasing the share of renewable energy and energy efficiency, with the result of creating also savings (SDG 7)
“Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all”with the improvement of resource efficiency in consumption and production as to endeavour to decouple economic growthfrom environmental degradation (SDG 8)
“Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation” (SDG 9)
“Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns”, using the natural resources efficiently, reducing the waste generation (including the food waste) and managing sustainably the chemical products (SDG 12)
“Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts”specially improving education, awareness raising and capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning (SDG 13)
“Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrialecosystems..” (SDG 15)
“Promotepeacefuland inclusivesocietiesfor sustainable development… and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels” highlighting the theme ofsocial justice(SDG 16).
c) LEAF: Learning About Forests wants to encourage environmental education through awareness raising among students, teachers and the wider school community, to increase knowledge about the key role forests play for sustainable life on our planet, reflecting their cultural, ecological, economic and social functions, with themes as biodiversity, climate, products or services, codes and myths.
The key Goals linked to the Learning About Forests programme are:
“Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”, increasing the number of youths and adults who have relevant skills and ensuring that all learners (referring to the whole school community) acquire knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including through education for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature (SDG 4)
“Ensure availability and sustainable management of water..”, protecting water-related ecosystems and supporting the participation of local communitiesfor improving water management(SDG 6)
“Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainable manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss”, ensuring a sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, including their biodiversity, in particular forests, wetlands mountains and drylands, preventing the extinction of threatened species(SDG 15)
The principles behind LEAF are compatible with the aim of more SDGs:
“End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promotesustainable agriculture”, implementing agricultural practices, such as the tree-planting events, which help maintain ecosystems and progressively improve land and soil quality (SDG 2)
“Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages” (SDG3)
“Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainableand modern energyfor all” (SDG7)
“Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment..”, endeavouring to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation and devising policies that encourage sustainable tourism which promotes local culture and products, such as jobs related to the forest, while learning to respect the forest community as well as its myths, laws and codes (SDG8)
“Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable”, strengthening efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage while supporting positive links between the urban and the rural areas as to widen the access to inclusive green and publicspaces (SDG11)
“Ensure sustainable consumption patterns” through relevant information and awareness for achieving sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources (SDG12)
“Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts” improving education and awareness raising on climatechange and the role of forests (SDG13)
“Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development” (SDG17).
d) BLUE FLAG: The world’s biggest voluntary eco-label for beaches, marinas and eco-tourism boats works towards sustainable development through compliance with criteria dealing with environmental education and information, environmental management, water quality, safety and other services.
The principles and rules of the programme comply with the content of many Goals:
“Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all”, improving water quality with pollution reduction and minimization of hazardous chemicals release, increasing recycling, safe reuse and water-use efficiency through the usage of sustainable withdrawals as to protect water-related ecosystems also with the support and participation of local communities (SDG 6)
“Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all”improving the resource efficiencyin consumption while devising and implementing policies to promote sustainable tourism which creates job, promotes local culture and products.Blue Flag focuses as well on the protection of labour rights together with the promotion of a safe and secure working environment and the prohibition of child labour (SDG 8)
“Build resilient infrastructure..”upgrading it as to be sustainable and equipped with clean technologies (SDG 9)
“by 2030 empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status”with the aim of reducing inequalities and discriminatory practices for wages as social protection policies (SDG 10.2)
“Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable”enhancing capacities for participatory and sustainable human settlements as to strengthen the efforts for safeguarding the world’s cultural and natural heritage while providing universal access to the public spaces particularly for women and children, older persons and persons with disabilities(SDG 11)
“Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns”for the efficient use of natural resources, through a sound management and reduction of chemicals and wastes and the promotion of sustainable public procurement practices (SDG 12)
“Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development”preventing and reducing marine pollutionalso from land-based activities, addressing the impacts of ocean acidification and conserving coastal and marine areas. Blue Flags also contributes in increasing the economic benefits to SIDS and LDCs with the sustainable use of marine resources through tourism (SDG 14)
“Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems… halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss” for halting the loss of biodiversity and preventing the extinction of threatened species, also through the integration of ecosystem values into local planning policies (SDG 15).
The implementation of the Blue Flag programme also work towards the aim of several more SDGs:
• “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages” (SDG3)
• “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”as education has a central role in the programme and reaches out for all the persons involved in it as well as for theusers (SDG4)
• “Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls”(SDG5)
• “Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable,and modern energy for all” to help increasing the share of renewable energy and energy efficiency(SDG7)
• “Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts”(SDG 13)
• “Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development..”enforcing non-discriminatory policies for sustainable development (SDG16)
• Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development”through a multi-stakeholder partnership, which involves also public partnersand local authorities,where knowledge and expertise are shared (SDG17)
e) GREEN KEY: This eco-label for tourism facilities (hotels, campsites, small accommodations, tourist attractions and restaurants) is a voluntary award that aims at contributing to prevent climate change and reach sustainable tourism by awarding and promoting best practice, with the goal of changing the environmental practices at the awarded establishments but also the behaviour of tourism actors, including guests, staff, suppliers, authorities, local communities so to involve them in increasingly safeguarding their own environment. The focus is on themes such as environmental management, water, waste and energy saving, involvement and awareness of guests and staff, management of food and beverage and open spaces.
For what concerns the part of the programme related to environmental management, the Goals mainly involved are:
“Ensure … sustainable management of water..” improving its quality, having the proportion of untreated wastewater, increasing recycling, safe reuse and sustainable withdrawals of freshwater (SDG 6)
“Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”setting rules for developing or upgrading quality infrastructures to support economic development and human well-being for an increased resource use efficiency and greateradoption of clean technologies (SDG 9)
“Make … human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable”paying attention to air quality, indoor environment and waste management as to tackle climate change(SDG 11)
“Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns”with rules for achieving sustainable management of natural resources,respecting eco-criteria for food and beverages, reducing waste generationand achieving environmentallysound management of chemicals (SDG 12).
This way the programme “develops and implements tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism which creates jobs, promotes local culture and products” (12.b).
As an eco-tourism programme focused on the environmental awareness of staff and guests, the Goals principally involved are:
“Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being..” where the programme has to encourage the users to take part in green activities (SDG 3)
“..ensure all learners acquire knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including among others through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights..” as part of the “educational Goal” (number 4), whereby the learners are the recipients of the environmental information expected in the implementation of the programme (SDG 4.7)
“Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all”, as the Green Key programme sets Corporate Social Responsibility and safety rules for the workers(SDG 8)
“Take urgent action tocombat climate change and its impacts”through a reduced environmental impact but also through the improvement of education and awareness raising for both the facilities’ staff and users (SDG 13)
“..revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development” (SDG 17).
Economic strengthening of Roma families
Project Economic strengthening of Roma families in the municipalities of Knjaževac and Ljubovija , under the Project „Technical Assistance to the Office for Human and Minority Rights in the implementation of the National Strategy for Roma Inclusion“ started on May 2015, supported by OSCE Mission in Serbia and having EASD as the Implementing Agency.
Project activities:
For your attention: 2015 ACUNS Conference
In June, 2015 the ACUNS Annual Meeting commemorates the 70th anniversary of the founding of the United Nations. In cooperation with our host institutions,The Hague Institute for Global Justice and the International Institute of Social Studies, ACUNS invites its members, and other interested scholars and practitioners, to join us in The Hague to engage in critical, informed discussions of the achievements, the deficits and the ongoing challenges of the United Nations system in nurturing, developing, promoting and defending ideas and practices of security and justice in global governance. We do so, as we also return to “The City of Peace and Justice”, where ACUNS last held an Annual Meeting in 1994.
The title for this year’s Annual Meeting clearly reflects aspirations rather than accomplishments, and should be understood broadly. Today, just as the nature and scope of the UN system’s activities have expanded greatly since 1945, so too security and justice and their intersection in global governance are taken to include a far wider array of concerns than were debated in San Francisco. Preventing and resolving conflicts, promoting international peace, and pursing new norms of global justice now also can involve issues of sustainable development, economic crisis management, climate change, human rights and gender, the rule of law and transitional justice, as well as conflict management and resolution. From wars and crises in Ukraine, Syria, Libya, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Gaza, to promoting efforts to prevent and stop violence against women everywhere, to highlighting the plight of small island states facing climate change-induced rises in sea levels, and responding to cross-border financial shocks, the UN system is called on frequently by Member States, NGOs and civil society organizations to assist or even to lead in global efforts to understand and address these problems. Too often, it is called on to do so when States and other bodies are themselves unable or unwilling to agree on the measures and resources needed, or sometimes even the cause(s) of the problems.
Plenary Titles
- The Role of The Hague Institutions in Promoting International Justice
- Balancing Law and Politics: What are the Tensions between Peace and Justice?
- The Future of Global Governance and the UN: Ensuring Security and Justice
- Global Equity and Global Justice: How Far will the SDGs Deliver?
EASD is ACUNS member. Prof Andjelka Mihajlov is in one of the ACUNS experts. Prof Mihajlov participated at ACUNS Vienna Conference , UN Colloquia Session II, 28 February 2011.
For your attention: Europa Diary in Serbian, p.51-61
Centre of the European Union publishes its fifth edition of the Europa Diary. Seventy six thousand copies of this specific textbook will be distributed to the 2nd grade students of all high schools in Serbia at the beginning of the 2nd semester. Europa Diary users are 2nd grade students in almost 500 four- and three-year high schools in Serbia. The Diary contents topics on Serbia’s European integration process, but also other topics that are important to the students, such as environment, consumer protection, sport, travel, and human rights. All topics are adapted to the age group. In addition to the Diaries 3,200 Teacher’s Guides will be delivered to the teachers. The Guides are designed to complement the Diary providing a selection of activities, worksheets and class preparations for the teachers. Serbian edition continues to be the only edition published outside the European Union and therefore the only edition in non EU official language. Europa Diary project is funded by the Delegation of the European Union to the Republic of Serbia and has been implemented in the schools for several years with the support of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology Development of the Republic of Serbia. A substantial support was also given of drafting some of the texts by the Office for European Integration of the Government of Serbia. A copy of this year’s edition of the Europa Diary and Teacher`s Guide is available on the EU Delegation website or EU Info Centre website .
Text from EU Delegation in Serbia.
In accordance with EASD Mission to environmental educate future EU citizens in Serbia (as the outreach of ENV.net Survey and “Serbia we want” process), we are sharing this publications, with special attention to p.51-61 of Europa Diary.